Quickjack is an intuitive, point-and-click tool for performing advanced and covert clickjacking and frame slicing attacks. It also allows you to easily perform clickjacking, or steal “clicks” from users on many websites, forcing the user to unknowingly click buttons or links (for example the Facebook Like button) using their own cookies. Quickjack By placing the […]
Archives for February 2018
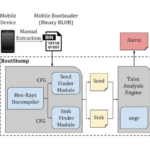
BootStomp – Find Android Bootloader Vulnerabilities
BootStomp is a Python-based tool, with Docker support that helps you find two different classes of Android bootloader vulnerabilities and bugs. It looks for memory corruption and state storage vulnerabilities. Note that BootStomp works with boot-loaders compiled for ARM architectures (32 and 64 bits both) and that results might slightly vary depending on angr and […]
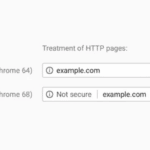
Google Chrome Marking ALL Non-HTTPS Sites Insecure July 2018
Google is ramping up its campaign against HTTP only sites and is going to mark ALL Non-HTTPS sites insecure in July 2018 with the release of Chrome 68. It’s a pretty strong move, but Google and the Internet, in general, has been moving in this direction for a while. It started with suggestions, then forced […]
altdns – Subdomain Recon Tool With Permutation Generation
Altdns is a Subdomain Recon Tool in Python that allows for the discovery of subdomains that conform to patterns. The tool takes in words that could be present in subdomains under a domain (such as test, dev, staging) as well as takes in a list of subdomains that you know of. From these two lists […]
0-Day Flash Vulnerability Exploited In The Wild
So another 0-Day Flash Vulnerability is being exploited in the Wild, a previously unknown flaw which has been labelled CVE-2018-4878 and it affects 28.0.0.137 and earlier versions for both Windows and Mac (the desktop runtime) and for basically everything in the Chrome Flash Player (Windows, Mac, Linux and Chrome OS). The full Adobe Security Advisory […]